Streamline property accounting with essential tips on tracking income, managing expenses, and setting up systems. Click to optimize your finances!

Understanding Property Management Accounting
Property management accounting involves the process of tracking and managing all financial transactions related to a rental property.
This includes income, such as rent payments and deposits, and expenses, such as maintenance costs, taxes, and utilities. Property management accounting also includes the financial planning necessary for running a property efficiently, ensuring the business remains profitable, compliant, and financially sound.
Key Responsibilities
Tracking Income: Monitoring rent payments, deposits, late fees, and other sources of income. Proper tracking ensures timely payments and helps maintain a healthy cash flow.
Managing Expenses: Keeping a detailed record of ongoing costs related to property management, such as maintenance, repairs, utilities, and taxes, to prevent overspending and manage the property’s budget efficiently.
Maintaining Records: Accurate record-keeping is essential for audits, tax filings, and reporting. Proper documentation ensures transparency and provides a clear overview of the property’s financial performance.
Now that we’ve defined property accounting let us look into the key financial concepts in property accounting that you absolutely need to know.
Key Financial Concepts in Property Management Accounting
Understanding key financial concepts in property management accounting is essential for maintaining the financial health of your property. Here are some of the most important terms and concepts:
Cash vs. Accrual Accounting
Cash Accounting: Revenue and expenses are recognised only when cash actually changes hands. This means that income is recorded when you receive rent payments, and expenses are recorded when you pay bills.
Accrual Accounting: Revenue and expenses are recognized when they are incurred, regardless of when the cash is exchanged. This method provides a more accurate picture of the financial health of the property since it accounts for income and expenses when they actually happen, even if payments are pending.
For example, income is recorded when rent is due, not when it is paid. This approach provides a more accurate picture of your business's financial health and is often preferred by larger property management operations.
Income and Expense Tracking
Tracking Rental Income: The core source of income for any rental property is rent paid by tenants. Managing this income efficiently, including handling deposits, late fees, and other charges, is critical to property management success.
Expense Tracking: Property expenses can include maintenance, repairs, utilities, insurance, property taxes, and management fees. Proper tracking ensures that you stay within budget and maintain profitability.
Basic Accounting Terms
Accounts Payable (AP): Money owed by the property manager to vendors or service providers for goods or services rendered, such as maintenance, repairs, or utilities.
Accounts Receivable (AR): Money owed to the property manager by tenants for rent, security deposits, and other fees.
Revenue: The income generated from rent, late fees, and any additional services (like parking or laundry fees).
Expenses: Costs incurred in the operation and maintenance of the property, including management fees, utilities, insurance, taxes, and repairs.
Depreciation: The reduction in the value of property over time due to wear and tear. Depreciation is an essential concept for tax purposes, as it allows property managers to deduct the depreciation value of the property over time from their taxable income.
Net Operating Income (NOI): This is the income generated from property operations after subtracting operating expenses (such as maintenance and property taxes) but excluding financing costs and taxes. NOI is a key metric for evaluating the profitability of a property.
Capital Expenditures (CapEx): These are large, one-time expenses for property improvements or purchases that increase the value of the property, such as a new roof, renovations, or major repairs.
Operating Expenses (OpEx): Ongoing costs related to maintaining and running the property, such as utilities, property management fees, cleaning services, and repairs.
Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM): A formula used to assess the value of a rental property by dividing the property’s purchase price by its annual rental income. It’s a simple method to evaluate whether the property is worth the investment.
By understanding and implementing these key financial terms and concepts, property managers can ensure they are making informed decisions, staying within budget, and ultimately ensuring the profitability and financial health of the property.
Next, let us look into how to set up a property management accounting system.
Setting Up Property Management Accounting System

Setting up a solid accounting system is essential for keeping your property’s financials organised and ensuring compliance with regulations. Let’s break down the key steps involved.
Open Separate Business Accounts
The first and most important step in setting up your property management accounting system is to separate business and personal finances. This is crucial for several reasons:
Clarity: Keeping your personal and business funds separate makes it much easier to track income and expenses for your property management business.
Tax Reporting: By maintaining separate accounts, you simplify tax filings, as it eliminates confusion between personal and business expenditures.
Compliance: Most tax laws require that personal finances be distinct from business finances. Keeping your accounts separate ensures that you comply with regulations and are prepared for audits.
Establish a Chart of Accounts
A Chart of Accounts (COA) is a structured list of all financial accounts used in your accounting system. It helps organise all income and expense items, making it easier to track financial transactions. Common categories in a COA include:
Income Accounts: Rent, parking fees, pet fees, and other charges.
Expense Accounts: Maintenance, repairs, utilities, property taxes, and insurance.
Asset Accounts: Property value, tenant deposits, and equipment.
Liabilities Accounts: Mortgages, loans, accounts payable.
Having a clear chart of accounts will allow you to easily track financial performance and simplify the process of generating reports for taxes, budgeting, and audits.
Now, let us delve into the essential processes in property management accounting.
Essential Processes in Property Management Accounting
Once your accounting system is set up, it’s important to establish key processes that will help keep everything running smoothly. Let’s go over the essential processes that should be in place.
1. Rent Collection and Tracking
Tracking rent payments is the most fundamental part of property management accounting. A clear and effective system should be in place to:
Track Rent Payments: Ensure all rent payments are recorded accurately, including any additional fees such as late fees or parking fees.
Manage Overdue Amounts: Set up a reminder system for tenants with overdue payments. Consider implementing late fee policies to encourage timely payments.
Online Rent Payments: Offering online payment options through property management software can simplify the collection process and reduce delays. It also helps tenants keep track of their payments and due dates.
Having an organized rent collection system ensures a steady cash flow, which is critical for the financial health of the property.
2. Expense Management and Documentation
Proper expense management is essential to avoid overspending and maintain profitability. Here’s how to manage expenses:
Track All Expenses: Maintain detailed records for each expense category, such as maintenance costs, utilities, property taxes, insurance, and repairs. This includes both one-time and recurring expenses.
Expense Documentation: Ensure all expenses are properly documented. Keep receipts, invoices, and contracts to support any deductions you claim for tax purposes. Using digital tools for organising these documents can make them easily accessible during tax season or audits.
Expense Recovery: If applicable, track expenses that can be passed on to tenants, such as utilities or maintenance costs. Ensure that these recoveries are documented properly.
Accurate expense tracking allows you to keep tight control of costs and ensures you are operating within budget.
3. Regular Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation is a critical process to ensure that the financial records align with the bank’s statement. Here’s how to maintain accurate records:
Frequency: Reconcile bank accounts on a monthly or quarterly basis to avoid discrepancies. This ensures that all deposits and payments have been correctly recorded.
Identify Discrepancies: If there are any discrepancies between your records and the bank statement, they need to be investigated and corrected immediately. This could be due to errors like missed payments or incorrect data entry.
Accurate Financial Records: Regular reconciliations help ensure that your accounting system is up to date, and it helps you stay on top of your cash flow.
This process ensures accuracy in your financial statements and prevents potential errors from compounding over time.
4. Financial Reporting and Budgeting
Lastly, generating financial reports and budgeting are key to making informed decisions and ensuring the long-term financial health of your property management business. Here’s what you need to focus on:
Generate Regular Financial Reports: Prepare and review financial statements such as Profit and Loss (P&L), Balance Sheets, and Cash Flow Statements. These reports help assess the financial health of the property and guide decision-making.
Budgeting: Use financial reports to create a budget that reflects both your income and expenses. Regularly update the budget to account for seasonal changes, unexpected repairs, or rent fluctuations.
Strategic Planning: Financial reports and budgets should be used for long-term strategic planning. They will guide decisions on property investments, maintenance planning, and rent increases.
These reports give you the insight you need to make data-driven decisions and improve the profitability and efficiency of your property management.
Next, it is important to understand financial statements and reporting.
Types of Financial Statements
There are three primary types of financial statements that every property manager should regularly generate:
Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of the property’s financial position at a specific point in time. It shows the relationship between:
Assets: What your property owns (e.g., property value, cash, equipment).
Liabilities: What your property owes (e.g., mortgages, loans, accounts payable).
Equity: The value of the property after liabilities are deducted from assets.
Income Statement (Profit & Loss)
The Income Statement, also known as the Profit & Loss (P&L) statement, shows your revenue and expenses over a specific period, such as a month or year. It provides a detailed picture of:
Revenue: Income generated from rents, fees, and other property-related services.
Expenses: Costs for property management, maintenance, taxes, utilities, and other operational expenses.
Profitability: The bottom line, showing whether the property is making a profit or incurring losses.
Cash Flow Statement
The Cash Flow Statement tracks the flow of cash in and out of your property management business, specifically focusing on:
Operating Cash Flow: Cash generated or spent in the course of regular property operations, such as rent payments and maintenance costs.
Investing Cash Flow: Cash spent or received from investments, like property purchases or sales.
Financing Cash Flow: Cash flows related to financing activities, such as loans or repayments.
Using Statements for Informed Decision-Making
Regularly reviewing financial statements provides valuable insights into the performance of your property management business. Here’s how you can use these reports for informed decision-making:
Monitor Performance: Use the income statement to track revenue trends, identify areas where expenses are increasing, and find opportunities to reduce costs.
Identify Trends: The cash flow statement helps you identify cash shortages or surpluses, enabling you to plan for future expenditures and ensure the business remains financially viable.
Strategic Planning: The balance sheet provides a clear view of your property’s assets and liabilities, helping you make decisions about financing, expansion, and investment strategies.
Now that we understand financial statements and reporting let us look into the best practices for property management accounting.
Best Practices for Property Management Accounting
To ensure your accounting system is efficient and effective, implementing best practices is key. Here are some strategies to streamline property management accounting and maintain financial health:
Using Software Tools to Automate Accounting Tasks
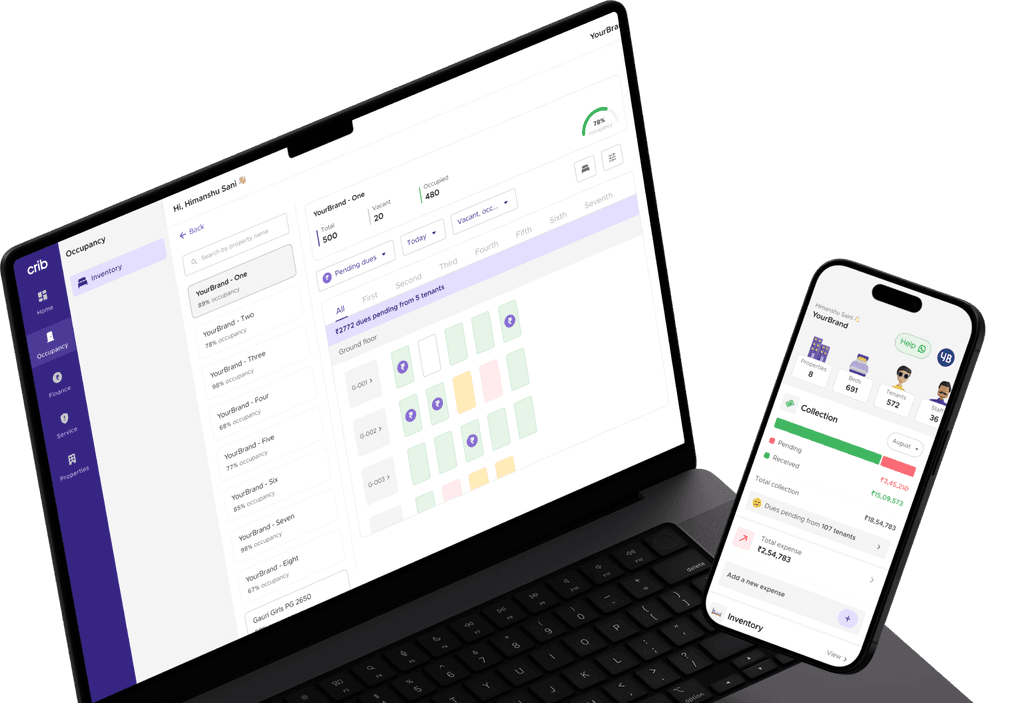
Automating accounting tasks is an essential step in improving efficiency and reducing the chance of errors. Using software like Crib can help property managers streamline daily accounting processes:
Rent Collection Automation: Crib can automate rent collection, sending reminders and tracking payments to ensure timely payments.
Expense Tracking: Automatically categorise and track property-related expenses like maintenance, repairs, and utilities, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Reporting: Generate financial reports (balance sheets, P&L, cash flow statements) with a few clicks, making it easier to assess your property’s financial health.
By leveraging automation, property managers can save time, reduce errors, and focus on strategic tasks rather than manual record-keeping.
Regularly Reviewing Financial Performance and Records
Regularly reviewing your financial performance is essential for identifying issues early and ensuring long-term profitability. Key practices include:
Monthly or Quarterly Reviews: Set aside time each month or quarter to review your financial statements, including P&L, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Identify Trends: Look for patterns in revenue and expenses. Are costs increasing in certain areas? Is income decreasing?
Adjust Strategies: Based on your financial review, adjust your strategies, such as rent pricing, cost-cutting measures, or investment decisions.
Regular reviews ensure that you stay on track to meet your financial goals and can quickly adapt to any changes in the property management environment.
By following these best practices, property managers can maintain accurate financial records, stay on top of taxes, and make strategic decisions that ensure the success and profitability of their business.
In the next section, we explore how to overcome the challenges in property management accounting.
Compliance and Taxation
Effective compliance and tax management are crucial aspects of property management accounting in India. Ensuring adherence to all relevant laws and regulations not only protects you from legal issues but also maximises financial efficiency.
Property-Related Tax Obligations
Every property manager in India must ensure compliance with various tax obligations, including:
Goods and Services Tax (GST): If rental income from commercial properties exceeds ₹20 lakh (₹10 lakh in some states), GST is applicable at 18%. Residential rental income is generally exempt but may be subject to GST in certain cases.
Property Tax: Timely payment of property tax to municipal corporations (such as MCD in Delhi, BMC in Mumbai, and BBMP in Bengaluru) is essential to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on Rent: Under Section 194-IB, individuals paying rent above ₹50,000 per month must deduct 5% TDS. For businesses, Section 194-I mandates a 10% TDS deduction on rent payments.
Income Tax on Rental Income: Rental income is taxable under ‘Income from House Property’, with deductions available under Section 24(b) for home loan interest and standard deduction (30%) on rental income.
Tax Deductions for Property Owners & Managers
Property managers in India can reduce taxable income by claiming deductions, such as:
Property Repairs & Maintenance: Expenses on repairs, painting, and regular maintenance are deductible under the Income Tax Act.
Depreciation Benefits: Depreciation on building structures can be claimed, reducing taxable income for property owners.
Home Loan Interest Deduction: Under Section 24(b), property owners can claim deductions up to ₹2 lakh annually on home loan interest for rented-out properties.
Property Management Expenses: Fees paid to property managers, brokers, or contractors for maintenance services are deductible.
Role of Property Accountants
Accountants play a vital role in tracking these deductions and ensuring compliance with tax laws. They help maximise tax benefits while lowering overall tax liability.
By leveraging professional accounting support and automation tools like Crib, property managers in India can simplify tax compliance and optimise their financial strategy.
Common Challenges in Property Management Accounting
Property management accounting comes with its fair share of challenges, especially when managing multiple properties, staying compliant with regulations, and handling tenant payment issues. Here are some common obstacles:
Managing finances across multiple properties efficiently.
Tracking income/expenses separately for individual properties.
Generating timely and accurate financial reports.
Staying updated with tax laws (GST, property taxes, deductions).
Complying with landlord-tenant regulations (Rent Control Acts, lease terms).
Adhering to accounting standards (Ind-AS, Income Tax Act).
Recovering overdue tenant payments.
Enforcing late fees without disputes.
Creating flexible payment plans for tenants in financial distress.
Maintaining clear communication to resolve payment issues proactively.
Next, let us look into compliance and taxation.
How Crib Simplifies Property Accounting

Incorporating automated software like Crib can streamline accounting tasks, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. Let’s explore how Crib can make property accounting simpler and more effective.
Automated Rent Collection and Invoicing
Crib automates the process of rent collection and invoicing, ensuring accurate and timely payments. With automatic reminders and secure online payment options, tenants can make payments without delay, and property managers can focus on more strategic tasks. The system also tracks overdue payments and applies late fees when necessary, maintaining a smooth cash flow.
Expense Tracking and Financial Reporting
Crib also simplifies expense tracking, helping property managers stay on top of operational costs. Whether it’s maintenance, utilities, or taxes, Crib automatically logs expenses and categorises them for easy reference. This streamlined tracking ensures that financial reports are accurate and that all expenses are documented for tax purposes.
Tax Reporting and Compliance
Crib’s automated system takes the stress out of tax reporting by generating tax-ready reports. These reports ensure that all deductions are properly documented and help property managers stay compliant with laws. Additionally, Crib provides accurate depreciation schedules, making it easier for property managers to take advantage of property-related tax deductions.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, effective property management accounting is crucial for ensuring financial stability, compliance, and profitability. By adopting automated accounting software like Crib, property managers can improve efficiency, reduce manual errors, and ensure that their financial records remain compliant with tax regulations.
Automation not only saves time but also provides real-time insights into the property’s financial health, enabling better decision-making and strategic planning. With Crib, property management accounting becomes more efficient, accurate, and compliant, ultimately leading to long-term profitability and business success.
Try Crib Today
Ready to streamline your property management accounting? Sign up for a free demo of Crib today and experience how our automated accounting solution can simplify your financial management.
Contact Crib for More Information
Have questions or need assistance with your property management accounting? Reach out to our team to learn how Crib can help simplify your accounting tasks and ensure your business stays financially healthy and compliant.